This is a guest post by Asif Taj, Technical Solution Architect – IP MPLS Networks & SD-WAN. We are grateful to him for sharing his expertise on our blog in order to help others.
Software Defined Networks: WAN and Branch Virtualization
Software Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) is a modern digital transformation technology with new paradigm shift in WAN that brings the benefits of Virtualization/Cloud to the Telecommunications Core Transport Network, Service Providers edge networks, Enterprises Networks (branch, HQ, DC) and Cloud Service Providers.
Service Providers across the globe are now adopting the SD-WAN technology in order to reduce CAPEX and OPEX, but also to increase the flexibility of their business.
SD-WAN is one of the most widely applied SDN concepts implemented to address obstacles in conventional networking environments of packet loss, jitter, delay, application and services performance. By replacing the MPLS with software defined network components, SD-WAN helps enterprises simplify branch offices setup, SME settings, HO and DC virtualization. In short, the WAN management is shifted to the software-defined cloud. An intelligently capable solution of SD-WAN shall support multiple connection types and network services including VPN, Firewall, WAN Optimization, Load Balancing, Application Delivery, Application based traffic steering and Access controls.
SD-WAN technology brings agility to the enterprise businesses using available options on-site at branch, remote site, headquarters, data centers of internet, WAN technologies options (MPLS, dedicated private leased lines, VPNs, LTE, Satellite) and a mix of internet and WAN to access global cloud based services, remote sites, private cloud at low cost with enhanced applications performance.
SD-WAN is a technology that distributes network traffic across wide area networks (WAN) and uses software defined networking concepts to automatically determine the route of the traffic that it takes to reach destination in a most effective way to and from the branch, remote, DC and HQ locations.
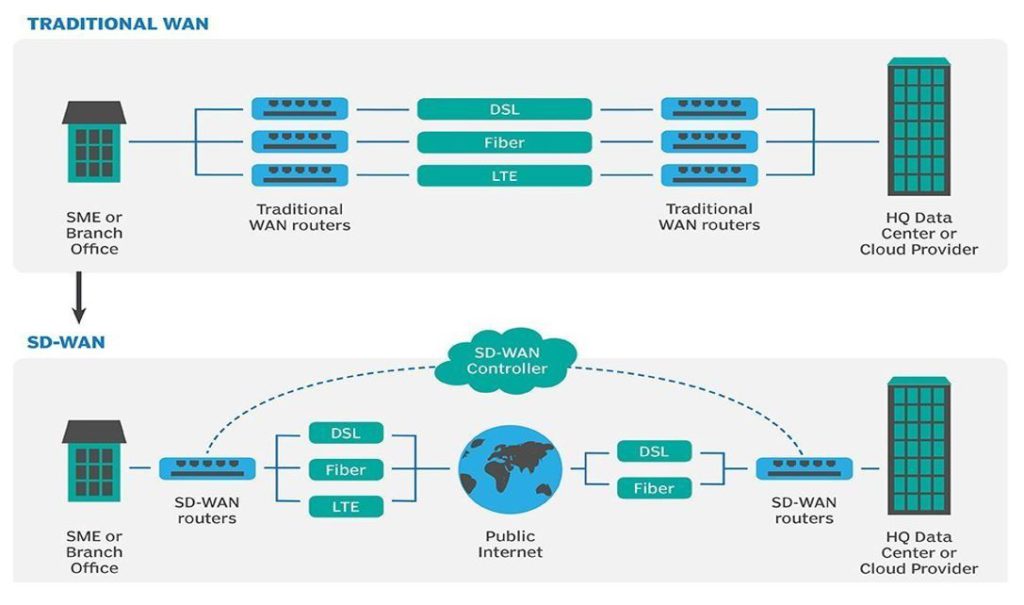
Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN Description
Applying software defined technologies to remote & branch sites, HQ, campus and data center networks simplifies network operations by consolidating multiple WAN technologies for connectivity, security, Wi-Fi, LAN networks functionality in a single platform that is easy to deploy, manage and troubleshoot.
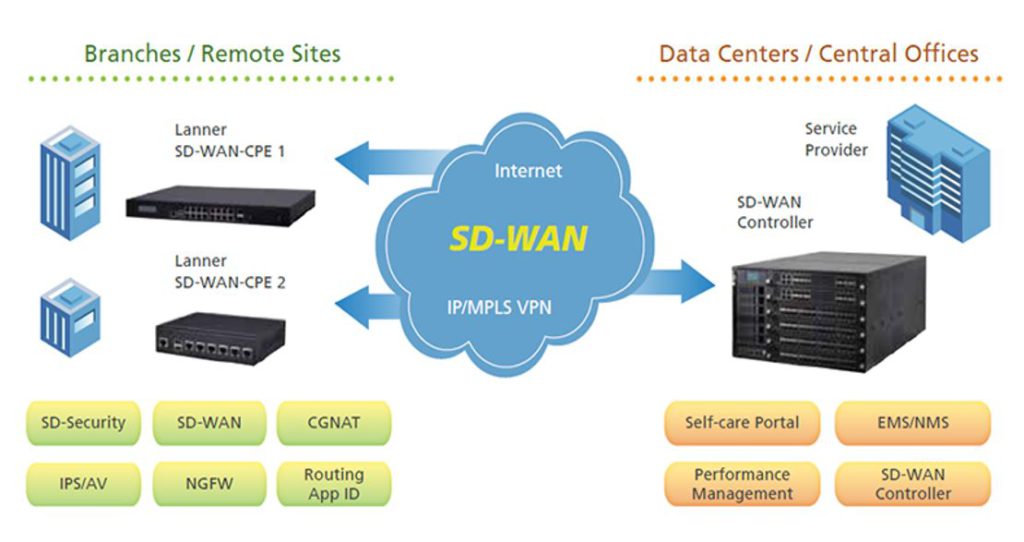
SD-WAN Network and Hardware Virtualized Service Support Functions
Most forms of SD-WAN technology create a virtual overlay that is transport-agnostic — it abstracts underlying private or public WAN connections i.e. MPLS, internet, broadband, fiber, wireless or Long Term Evolution (LTE). Enterprises can keep their existing WAN links, while overlay SD-WAN uses the multiple tunnels to optimize bandwidth by directing WAN traffic along the best route to and from branch offices and data center sites. SD-WAN technology centralizes network control and enables agile, real-time traffic management over these links.
SD-WAN is managed by a centralized controller / orchestrator platform. The software enables IT and networks staff to remotely program edge devices and reduce provisioning times, thus minimizing or eliminating the need to manually configure traditional routers in branch locations. Monitoring, Big Data Analytics, Management are the inherent features of the SD-WAN solutions. Providers also leverage the function of SD-WAN Cloud gateway’s to manage the services to their customers in a specified region.
While SD-WAN products and services vary among providers, most are based on one of two types: overlay SD-WAN or network as a service. With an overlay SD-WAN, a vendor provides an edge device to the customer that contains the software necessary to run the SD-WAN technology. For deployment, the customer plugs its WAN links into the device, which automatically configures itself with the network.
Providers that offer SD-WAN as a type of Network as a service (NaaS) enable their customers to access their own private networks. SD-WAN functionalities, like traffic prioritization and methods for WAN optimization, are incorporated into the service.
Software Defined Branch (SD-Branch) is a single, automated, centrally managed software-centric platform that replaces or supplements an existing branch network architecture. A natural successor in the evolution of software-defined wide area networks (SD-WANs), SD-branch simplifies the process of branching networks by collapsing multiple software-defined network functionalities, including routing, onto a single platform.
SD-branch technology relies upon:
- A virtualized internet protocol (IP) services platform that provides cloud-like elasticity, service chaining and programmability.
- A broad set of virtual network functions (VNFs) to deliver extensive networking and security IP services.
- A centralized management framework that allows integrated control, management, analytics and workflow.
Networking the remote or branch office (ROBO) is a critical, yet challenging, element for most centralized information technology (IT) organizations. SD-branch offers advantages in terms of rapid deployment (branch-in-a-box), lower hardware costs and operational expenditure (Opex) benefits. Other benefits of SD-branch technology include:
- Improved operational agility.
- Virtualized network functions feature of various network & security hardware.
- Centralized control of branch office’s network through single management pane.
- Smaller hardware footprint.
- Lower power consumption.
Most of the enterprises remote site/branch functions are hardware centric, and they needed different hardware appliances to deploy each of the functions. Enterprises now really don’t need any of those separate hardware appliances instead can run the virtual instances as a separate functions on a single device platform.
It is expected that many organizations will phase out their existing branch routers in favor of SD-WAN packages over the next few years and customers will have the option to buy and use SD-branch services with support for broader network features, including SD-WAN, routing, switching, security and Wi-Fi. For organizations choosing managed SD-WAN from a service provider, options will be defined by the service provider.
Software Defined Security (SD-Security) is a software defined architecture where security oriented VNFs and policies are implemented on gateway devices. Protection and Policy compliance of an organization are built by software approaches, while the reliance of enterprises on the physical hardware is minimized. SD-security enables a more adaptive, agile and scalable security infrastructure by using programmable open source software policies and open-standard v-CPE appliances, simplifying the deployment processes in branch offices and remote sites.

For optimal SDN implementations, SD-security should be accompanied with SD-WAN and intelligent deployment of software defined security architecture shall consist of mechanisms like zero touch provisioning (ZTP) and automatic service chaining. Segmentation is an essential component of SD-WAN security. This method enables enterprises to isolate, prioritize and assign network traffic. If traffic from an unknown device requests access to the network, IT staff can assign network policies to automatically route that traffic through a firewall first. Also, IT staff can prioritize high-priority traffic so it always travels on a specific link.
Most SD-WAN vendors also incorporate security features such as authentication, encryption or security certificates features for IPSec VPNs into their services to authenticate and verify network traffic.
SD-WAN services include a management console or interface to manage traffic, assign policies, and configure devices and sites. This interface also helps increase end-to-end network visibility.
Additionally, many SD-WAN vendors partner with security companies to integrate those security services with SD-WAN technology.
SD-Security provides features like UTM (Unified Threat Management), IDS and IPS, URL Filtering, NG-FW (Next Generation Firewall), DPI (Deep Packet Inspection), Access Control and Application based security as well in a single platform. Enterprises can use all of the features depending upon the licenses provided by their vendor.
Some vendor providing all of these feature with a separate license for advanced security and firewalling features. Thus virtualizing the network security functions providing ease of management and control over the traffic for the enterprise IT staff.
BENEFITS: SD-WAN improves application performance through a combination of WAN optimization techniques and its ability to dynamically shift traffic to links with bandwidth sufficient enough to accommodate each application’s requirements.
SD-WAN uses automatic failover, so if one link fails or is congested, traffic is automatically redirected to another link. This, in turn, further boosts application performance and reduces latency.
SD-WAN architecture enables administrators to reduce or eliminate reliance on expensive leased MPLS circuits by sending lower priority, less-sensitive data over cheaper public internet connections, reserving private links for mission-critical or latency-sensitive traffic, like VoIP. The flexible nature of SD-WAN also reduces the need for over-provisioning, reducing overall WAN expenses.
Ideally, SD-WAN simplifies the network by automating site deployments, configurations and operations.
Adding the SD-branch and SD-security capabilities gives enterprises an added flexibility to add up remote branch sites in a matter of couple of days and secure their data, traffic with controlled accessibility managed through the central location using controllers.
Enterprises can use SD-WAN, branch and security aspects as an overlay on top of the existing legacy hardware centric network or can replace legacy network with SD-WAN in a phased-wise transition.
The most important aspect of moving the data to the cloud is the security and utilizing the SD-security features using virtual network functions on a single platform gives flexibility and agility to enterprise businesses in terms of application, services deployment and performance with a secure and controlled access to cloud, data centers, sites and data. SD-security incorporates IPSec/GRE based VPN tunnels methods for control and data traffic.
In case of any queries or feedback, please drop a comment below and or connect with the author on LinkedIn.
References:
[1]. https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/WAN-optimization-WAN-acceleration
[2]. https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/IPsec-Internet-Protocol-Security
[3]. https://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/definition/VoIP
[4]. https://www.sdxcentral.com/networking/sd-wan/definitions/software-defined-sdn-wan/
[5]. Foundation of Modern Networking – William Stallings – Chapter 3
[6]. Versa Networks
[7]. IORoutes own observation, guidelines
Asif Taj
Latest posts by Asif Taj (see all)
- SD-WAN: Digital Transformation with SDN - March 21, 2019

Great article. Could you let me know some good resources to learn more about SD-WAN. Ty.
Thanks, Srikanth. SD-WAN courses from INE are pretty good, they would definitely give you an excellent insight into this new technology.